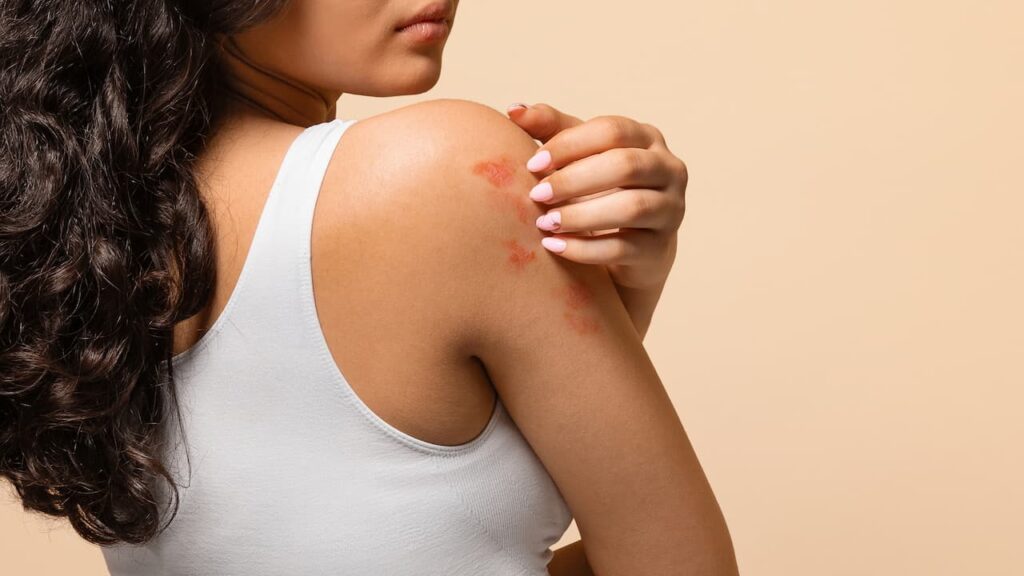
Eczema and psoriasis are chronic skin diseases that may seem similar, both causing redness, itching and skin lesions, but they arise from different causes, require different treatments and affect specific areas of the body.
It’s important to note that none of these diseases are contagious or develop due to poor hygiene.
Throughout the article, we’ll help you understand the differences between these two conditions.
Key points of the article
- Differences between eczema and psoriasis: causes, symptoms and affected areas
- Types of eczema and main aggravating factors
- How to identify and treat psoriasis
- Daily care and ways to prevent outbreaks
- Treatments available: from hydration to immune therapies
- Real testimonies from people living with these diseases
- When you should see a dermatologist.
What is eczema?
To put it in context, eczema (also known as atopic dermatitis) is an inflammation that causes dryness, irritation and a lot of itching, appearing in alternating periods of flare-ups and remissions. It is one of the most common skin conditions, especially in babies and children, but can appear in adulthood.
There are two types of eczema:
1. Atopic Dermatitis
Cause: genetic / immunological
Usual age: childhood
Location: folds, face, hands
Duration: chronic
Symptoms: itching, redness, dryness
2. Contact dermatitis
Cause: external substance (allergen or irritant)
Usual age: any age
Location: direct contact area
Duration: transitory (if the agent is avoided)
Symptoms: redness, blisters, itching
Causes of eczema
These causes are not entirely known, but involve various genetic and immunological factors as well as certain environments. People with eczema have a more fragile skin barrier, which makes it easier for allergens to enter and there are some factors that facilitate its appearance.
Common factors:
- Allergies (dust mites, pollen, food)
- Cold and dry weather Stress
- Synthetic clothes or aggressive detergents
- Genetics.
Symptoms of eczema
- Redness and dryness of the skin
- Intense and persistent itching
- Cracks and scabs
- Injuries located in the folds of the body (elbows, knees, neck).
Symptoms of eczema
The most important step is to deeply moisturize your skin to reduce inflammation. However, in more serious cases, medication may be necessary.
Examples of treatment:
- Emollients and moisturizing creams
- Topical corticosteroids
- Antihistamines (to relieve itching)
- Avoid triggering factors
Prevention of eczema
In order to prevent eczema outbreaks:
- Follow the treatment plan recommended by your dermatologist
- Avoid scratching the affected areas to avoid aggravating the lesions
- In colder weather, protect your hands with gloves
- Use gentle products and dry the skin with light touches, without rubbing
- Moisturize your skin several times a day (especially after showering)
- Prefer showers with lukewarm water
- Drink water throughout the day to keep your skin hydrated from the inside
- Wear clothes made of cotton or natural, breathable fabrics
- Avoid sudden changes in temperature and contact with irritating substances Reduce stress with activities such as walking, meditation or yoga.
Testimonials from people living with eczema
“We feel sorry for ourselves, it’s inevitable. Although, at the same time, we also feel particularly strong for being able to deal with something like this and overcome it every time.” – Ana Paula Correia
Read the full article – taken from “Saberviver”
“I don’t know what the future holds, but I have hope.” – Tânia Fernandes (about her 2-year-old son, Lucas)
What is psoriasis?
Psoriasis is an autoimmune and inflammatory disease in which the immune system accelerates the production of skin cells. This process causes the appearance of thick, reddish plaques covered in whitish scales.
In Portugal, it is estimated that there are more than 200,000 people with psoriasis according to the Portuguese Psoriasis Association. Globally, the disease affects more than 125 million people, with around 14 million in Europe, according to international estimates.
Causes of psoriasis
The most likely cause of psoriasis is genetic and immunological factors. It is not contagious, but can be triggered or aggravated by external factors.
Common factors:
- Physical or emotional stress
- Infections (e.g. tonsillitis) Certain medications (such as beta-blockers)
- Skin lesions (Koebner effect).
Symptoms of psoriasis
- Red plates with white or silver scales
- Thick, well-defined lesions
- May affect nails (changes in color and texture)
- Joint pain or stiffness (in cases of arthritic psoriasis).
Psoriasis treatment
Psoriasis treatment aims to: reduce inflammation, slow down cell renewal and relieve symptoms.
Common treatments:
- Creams with corticosteroids or calcipotriol
- Phototherapy (controlled UV light)
- Immunomodulatory drugs (in moderate to severe cases)
- Moisturizing and moderate sun exposure.
Psoriasis treatment
To prevent outbreaks of psoriasis, you should:
- Control stress Moisturize your skin daily
- Avoid skin lesions
- Moderate alcohol intake and don’t smoke
- Be careful with certain medications
- Controlled exposure to the sun
- Eat a balanced diet.
Testimony from someone living with psoriasis
“We go through various phases in terms of accepting the disease and I think I’ve been in the acceptance phase for a while now.” – Rita Felgueiras, 37
Read the full testimonial – “In your skin”
“I don’t know if I’m bothered, if I’m sad… but I wish I wasn’t.” – Luís Carmo, 46
Eczema vs Psoriasis: What are the main differences?
Although they share symptoms such as itching and redness, eczema and psoriasis have some differences:
- Appearance of the lesions: psoriasis has thick plaques with scales, while eczema presents as inflamed, dry and itchy skin
- Location: eczema tends to appear in the folds of the body, while psoriasis affects exposed areas such as the knees, elbows and scalp
- Origin: eczema is more associated with allergies and sensitivities; psoriasis is an autoimmune disease.
Analyzing and being aware of these differences makes it easier to identify the problem and start the right treatment.
When should you see a dermatologist?
It’s best to see a dermatologist if you notice skin lesions that won’t go away, persistent itching or discomfort. Being followed up by a professional will help you to be diagnosed correctly and receive the most appropriate treatment.
Seek medical help if:
- Symptoms interfere with your sleep or daily activities
- Lesions spread or worsen rapidly
- The usual treatments aren’t working You feel pain or signs of infection.
Whether it’s eczema or psoriasis, these inflammatory skin conditions can affect comfort and self-esteem. However, with the right diagnosis, medical monitoring and daily care, it is possible to control symptoms and significantly improve quality of life.
Important links on this subject:
The content of this blog is informative. They are not a substitute for medical diagnosis or treatment. Always consult a health professional.